Papillomas and condylomas are small viral growths on the skin. You need to be able to identify potentially dangerous devices in order to detect them in a timely manner and take the necessary measures. The main thing that distinguishes papilloma from condyloma is the type of virus.
Causes of neoplasms
There are more than a hundred different strains of human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV enters the body through domestic contact or unprotected sex. It can be transmitted from mother to child through the birth canal.
The appearance of growth indicates the rapid division of cells in the basal layer of the skin. It occurs under the influence of the virus, the activation of which is often associated with a decrease in the immune system. Depending on the strain, papillomas or condylomas appear on the body.
Characteristics of papillomas
Papilloma is a benign tumor that does not cause any discomfort, except for aesthetics. Characteristics of papillomas:
- soft homogeneous structure;
- presence of legs;
- small size (up to 10 mm in diameter);
- moderate pigmentation.
Papillomas are located anywhere on the body, except the mucous membranes of the genitals. As a rule, the color of the growth varies from the natural color of the skin to shades of pink, but highly pigmented papillomas are still not a pathology. Hair growth on the body of a papilloma is a normal part of life.
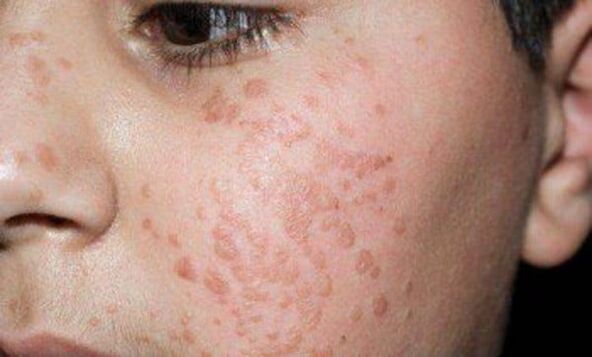
Papillomas are not dangerous if they do not interfere with the patient and do not cause accidental injuries in daily life. The emergence of this type of plant is due to the action of 2, 7 and 28 viral strains. You can get these types of HPV in your daily life and sexually.
Features of genital warts
Warts are divided into two types - pointed growth and broad. The first type occurs with HPV infection and is one of the symptoms of widespread syphilis.
The sites of genital warts are mucous membranes, mainly the urogenital area, as well as skin folds that are subject to abrasion against clothing.
The structure of the genital wart is papillary. The formations are attached to a thin stalk, and the plants are nourished by small roots and capillaries. Unlike papillomas, condylomata are often inflamed and can cause ulcers.
Genital warts are caused by strains 16, 18, and 54 of the virus. These types of HPV are potentially dangerous, especially for women. There is a direct link between these types of viruses and the development of cervical cancer. Infection occurs through sexual intercourse.
How to distinguish papilloma from genital warts?
The external differences between adults can be easily seen in the picture - papillomas are homogeneous, and condylomas have a small papillary structure.
- The difference between a papilloma and a wart is in the color of the growth. Papillomas can be highly pigmented, the color of the wart is usually light and does not differ from the mucous membrane.
- HPV, which causes the development of papillomas, is transmitted through household contact, personal hygiene, and even hand-to-hand contact (in the case of skin microtraumas). Warts are only sexually transmitted.
- The warts become inflamed. Papillomas can grow and show signs of inflammation and become damaged, but only as a result of traumatic effects.
- The shape of papillomas is mainly a round or oblong "head" located on the soft stem. Condylomata have irregular contours that can be arranged in clusters. Genital warts are characterized by narrowing from the stem to the end, which allows them to be distinguished from papillomas.
- The formation of different plants depends on different strains of the virus.
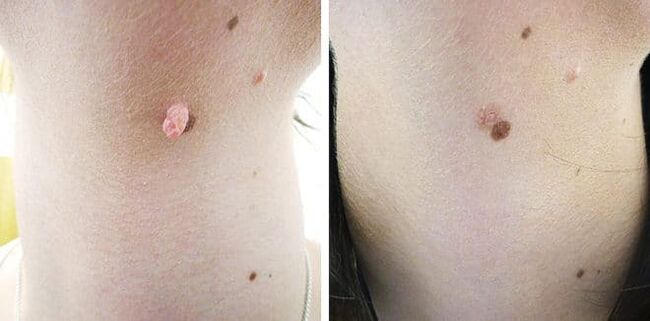
The main difference between a papilloma and a wart is that the growth of the genitals and mucous membranes must be eliminated.
Why are plants dangerous?
Papillomas and condyloma are conventionally safe tumors of the skin, but in the latter case there is a high risk of damage to the cells that are harmful to the cells.
Condylomata are skin manifestations of oncogenic forms of the virus. Many years of research have found a link between HPV and cervical cancer. Timely diagnosis with further removal of genital warts significantly reduces the risk of cancer in women.
Adults can be located not only on the skin and external genitalia, but also in the vagina and cervix. Due to the circulatory characteristics of the genitals, condyloma is poorly nourished and can grow rapidly. In gynecology, there are cases when warts on the walls of the vagina grow up to 10 cm in diameter.
Indications for exclusion
Warts should be removed, even if they do not cause discomfort. This is primarily due to the risk of infection of the sexual partner.
Removal of papillomas on the skin, whether or not, is an individual matter for each patient. The risk of developing papillomas into cancerous neoplasms increases when the growth organ is damaged. This can be caused by rubbing on clothes, accidental nails or detergent during hygienic procedures.
You should consult a dermatologist if:
- papilloma greatly enlarged;
- feels uncomfortable when walking;
- bleeding or purulent discharge is observed;
- The skin around the growth becomes inflamed.
Removal of construction — within five minutes. The procedure is almost painless. It is important to understand that early diagnosis can detect the onset of cell damage in a timely manner and stop the development of oncology.
How will the buildings be removed?
Any skin growth should be professionally removed. Self-cauterization of popillomas with the help of folk remedies is not always effective. Removal of genital warts at home is strictly prohibited.

A number of examinations should be performed before the procedure. First, the patient's blood is examined to determine the type of virus that caused the neoplasms.
Patients with multiple condylomata are prescribed antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy. This will stop the spread of the virus and help the immune system to fight HPV. Oils containing immunostimulants (such as interferon-based drugs) can help to get rid of genital warts. These drugs are in the form of suppositories, which allow you to successfully fight the growths on the walls of the vagina.
Methods of removal of structures:
- cryodestruction;
- electrocoagulation;
- laser burning;
- removal with a radio knife;
- Remove with a scalpel.
When a genital wart is removed, the tissue from the procedure is sent for histological analysis. For this, surgical incision or laser removal is indicated.
Electrocoagulation is the removal of neoplasms. This method has worked well for removing small papillomas.
Cryodestruction is used to remove skin neoplasms, but not on mucous membranes. Liquid nitrogen is used for growth that causes cell necrosis, and the papilloma simply disappears.
Radiofrequency ablation or radio knife is an effective and almost painless method of removing warts on the genitals. Under the influence of radio waves, the cells of the neoplasm are destroyed. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
Laser burning of the bones of the genitals is shown in the presence of a large number of growths. The advantage of this method is the cauterization of the vessels and capillaries that feed the formation. As a result of exposure, there are no traces on the skin, the risk of bleeding is eliminated. Complete recovery occurs within 5-7 days after removal of the epidermis.
Folk remedies for the removal of genital warts are not used because of the high risk of damage to the mucous membranes by aggressive components. Alkaline pharmaceuticals are also prohibited.
An image can help you to distinguish warts from papillomas. If genital warts form, it is recommended that you see a doctor and do not try to remove them yourself.














































































